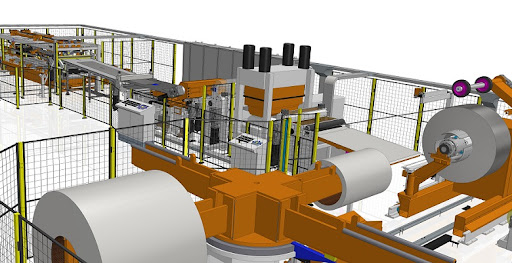
In the world of industrial manufacturing, particularly in metal processing, flying shears have become an indispensable part of the process. These machines offer a unique solution for cutting materials like steel or aluminum without stopping the production line. But what exactly is a flying shear, and why is it so widely used? Let’s break it down in a simple and understandable way.
What is a Flying Shear?
A flying shear is a machine that cuts moving material without requiring the production line to stop. Imagine you’re cutting a piece of paper with scissors. You usually hold the paper steady and cut it. Now, imagine the paper is moving—if you want to cut it without stopping, you’d need to move the scissors at the same speed as the paper. That’s the basic principle of a flying shear.
In a factory setting, long strips of metal are continuously fed through machines, and stopping the line for each cut would waste time and reduce productivity. A flying shear moves along with the material, cutting it at the precise moment without interrupting the flow.
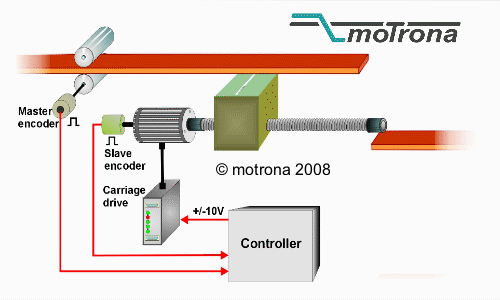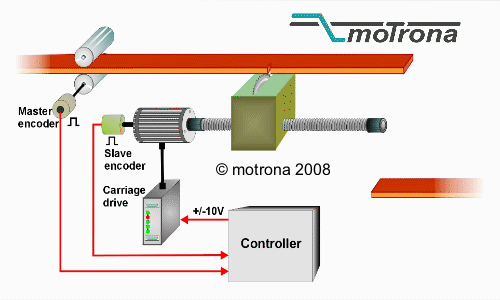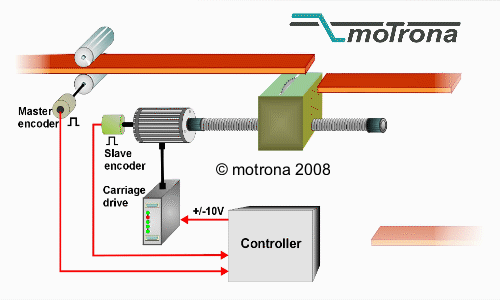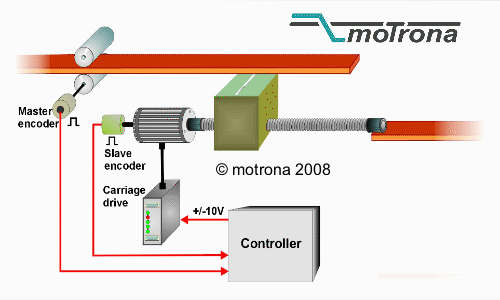
How Does a Flying Shear Work?
Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how a flying shear operates:
- Material Moves Along the Production Line: Large sheets or strips of material (usually metal) move continuously along the production line at high speeds.
- Shear Synchronization: The flying shear machine is synchronized with the speed of the material. This is crucial, as any mismatch in speed could lead to an uneven cut.
- Shearing Action: Once the shear is synchronized with the material speed, the blades of the shear move in to cut the material.
- Return to Starting Position: After making the cut, the shear returns to its original position to prepare for the next cut, while the material continues moving uninterrupted.

Key Technical Terms Explained
To better understand the operation of a flying shear, let’s break down some important technical terms:
- Blade Clearance: This refers to the gap between the cutting edges of the blades. It’s important to have the correct clearance for clean cuts, especially when working with thick materials. A small clearance is needed for thin materials, while a larger one is required for thicker materials.
- Cutting Speed: This is the speed at which the shear moves to cut the material. It needs to match the speed of the material on the production line. If the shear moves too slow or too fast, it could cause jagged or imprecise cuts.
- Synchronization: This refers to how well the shear matches the speed of the moving material. A well-synchronized shear ensures a clean, precise cut every time. In modern flying shears, this synchronization is achieved using complex control systems that continuously adjust the speed and position of the shear.
Applications of Flying Shears
Flying shears are widely used across several industries, but they are particularly common in metal processing. Below are some key applications:
- Steel Manufacturing: In steel plants, flying shears are used to cut long strips of metal into smaller sections for further processing. These machines can handle extremely high speeds, making them ideal for large-scale steel production.
- Aluminum and Copper Processing: Similar to steel plants, flying shears are used in aluminum and copper production lines. They cut the material into manageable sizes without stopping the continuous casting process.
- Packaging Industry: Flying shears are also used to cut flexible materials, such as plastic or cardboard, in high-speed packaging lines.
Why is it Widely Used?
The main reason for the widespread use of flying shears is their ability to improve production efficiency. By cutting materials without stopping the production line, factories can maintain high output rates while minimizing downtime. Additionally, flying shears are highly versatile—they can handle a wide range of materials, from thin sheets of aluminum to thick steel slabs, making them suitable for various industrial applications.
In modern manufacturing environments, flying shears are also equipped with advanced control systems. These systems ensure that the shear is precisely synchronized with the material flow, which results in cleaner cuts, less material waste, and fewer maintenance issues.
Conclusion
Flying shears play a crucial role in today’s high-speed manufacturing environments. Their ability to cut materials on the fly without stopping the production line makes them essential in industries like steel, aluminum, and packaging. As technology continues to advance, flying shears are becoming even more efficient, reliable, and easy to control, ensuring that they will remain a key piece of equipment in industrial production for years to come.
*https://pescheldynamics.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/flying-shear.gif
**http://softmc.servotronix.com/wiki/Flying_Shear_Application